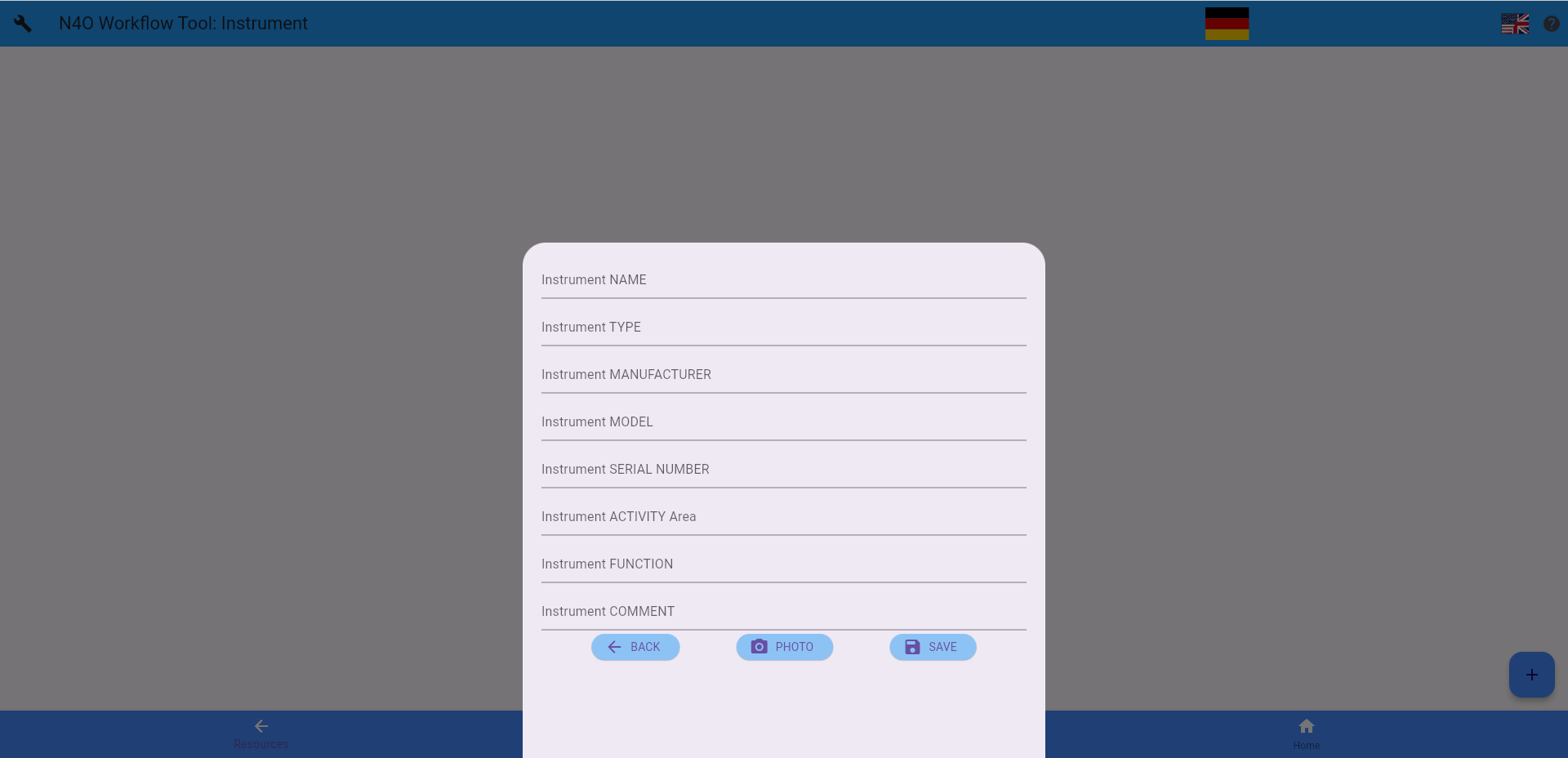
“Instruments” (formerly “equipment”) and “tools” are the basic hardware resources available for performing any of the “experiments.”
“Experiment” in this context means a process of using some combination of “instruments” and/or “tools” to do something to some combination of “compounds” and/or “substances.”
“Instruments” simply require more information than “tools.”
Instrument fields currently include:
- Name
- Type
- Manufacturer
- Model
- SerialNumber
- ActivityArea
- Function
- Comment
In addition, these might have a number of possible settings which affect performance: a microscope will have magnification and illumination settings, for example, and during the course of an experiment the user will have to choose which of these to use, even if specific choices are not made while the experiment is being designed.
Or a kiln might be capable of operating over a range of temperatures, but the “experiment” itself is only intended to see how a given type of clay reacts when fired at a specific temperature.
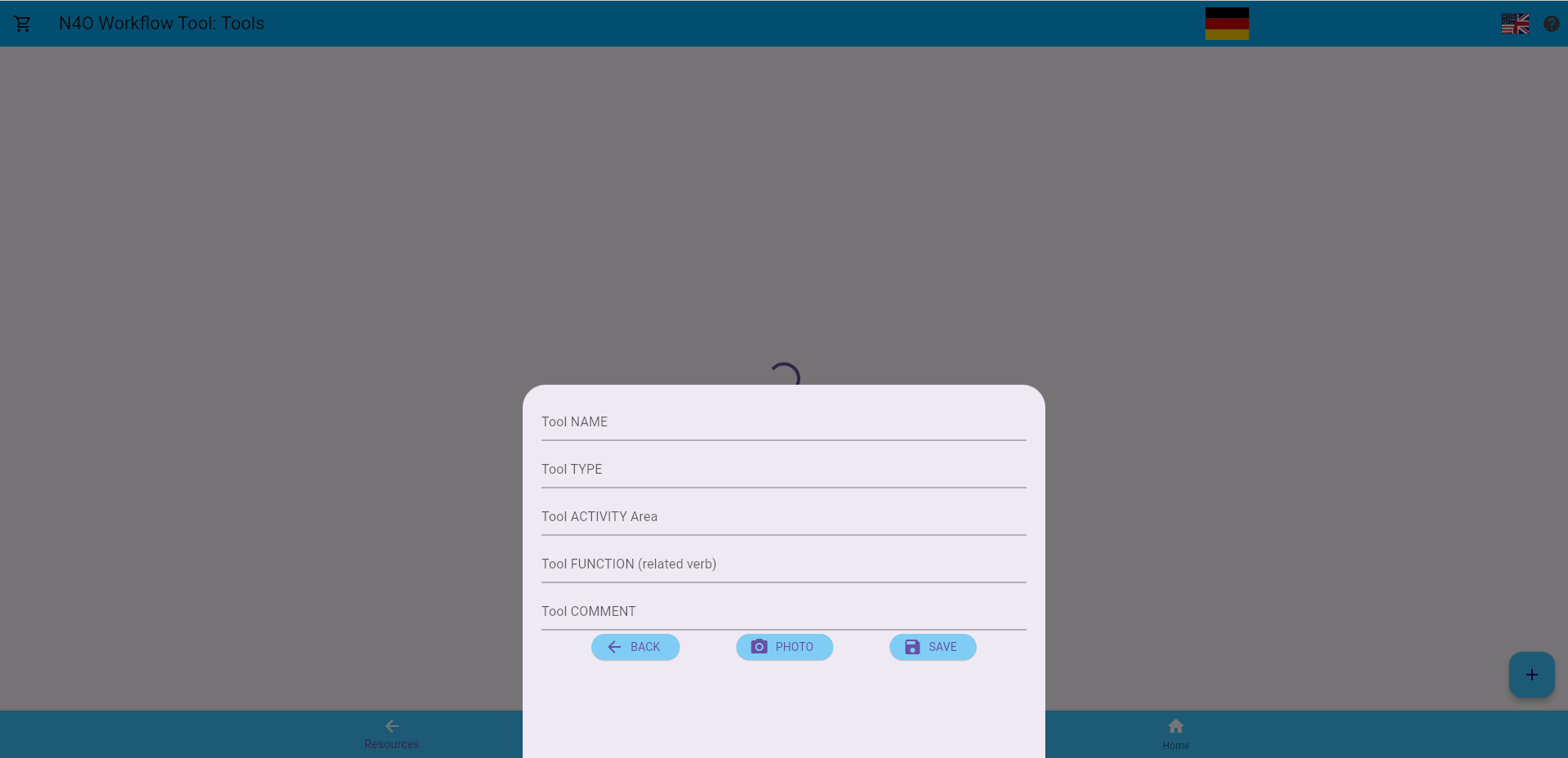
Tool fields currently include:
- Name
- Type
- Activity Area
- Function
- Comment
Examples of tool “names” include “hammer,” “saw,” “drill,” etc., and types of “hammers” would include “sledge,” “carpenter’s,” etc.; “saws” could include “table,” “band,” “cross-cut,” etc. Lists of all the possible types of tools are probably available somewhere, but the user will only need to enter an inventory of the tools available to him/her.
“Activity area” and (intended) “function” are complicated. Some tools and/or instruments have specific purposes: a microscope is only intended to magnify things, but a tool like a hammer can have a “general” use (hitting anything that needs to be hit) or specific “function” according to its “activity area” (“woodworking,” “ceramics,” “microscopy,” “glass production,” etc.). So (intended) “function” can then imply a specific activity: a “hammer” is intended to “hammer” nails (i.e. a simple “substance”). Some of this will be limited because a microscope, for example, will generally only be used for “observations” and not as part of a “reconstruction” or “re-enactment” process, but nesting and allowing for multiple functions could make programming… interesting.
It will be possible to photograph instruments and tools.
Resources:
- Institution
- Personnel
- Instruments and Tools
- Compounds and Substances
- References
Experimental design:
- Experiments
- Observations
- Measurements
- Reconstructions
- Replication
- Re-enactment
- Recipes
Tasks and Flowchart:
Demo version:

